Photo by Bigstock photo

Later the technique was further developed by fusion guitarist Frank Gambale.
The quality of sweep picking is that it produces a fast and fluid sound (once you get the hang of it). This is because you only need few strokes as apposed to alternate picking.
While it is generally used for arpeggios, it can also be applied to scales, 3 notes per string licks and… well just anything really.
In this topic we’ll be covering 5 pentatonic patterns in the key of A. If you already know how to play the 5 pentatonic shapes using alternate picking and you want to try sweep picking for a change to make it sound more fluid, give it a more Gambale feel to it or just to see where it will take you, this one’s for you.
You don’t have to choose one picking technique for your style of playing. A lot of guitar players combine both. They use alternate picking mainly and apply sweep picking occasionally for particular licks or arpeggios.
Sweeping
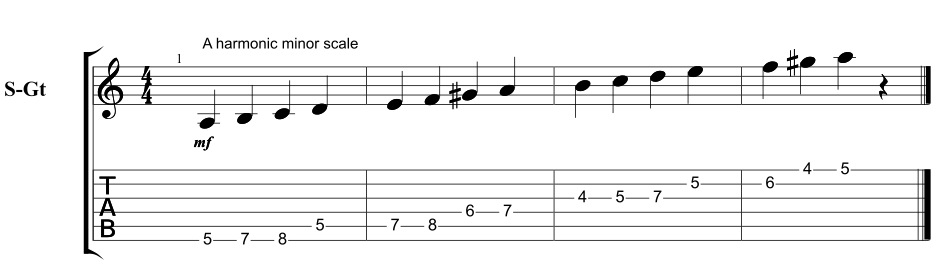
For the alternate picking approach you go “down, up, down, up, down, up” with the picking hand. In the scale patterns below you also use alternate picking except when changing strings you’ll be picking in the direction of where you’re heading. Use a downstroke if you’re changing to a higher (pitch) string and use an upstroke if you’re changing to a lower (pitch) string.
You can see the down and upstroke symbols in the scale patterns right between the standard and tablature notation. The downstroke symbol looks like a hurdle for track and field, the upstroke symbol looks like a “V”.
I have to admit the pentatonic patterns are quite a stretch. Major scales are much easier to play, but for the rock and blues players out there we don’t want to miss out on the pentatonic.
It takes a bit of practice to get used to the sweep picking feeling but hang in there. After a while it feels so natural and easy. It’s the path of least resistance.
Have fun!
Continue Reading
 Whenever you try to deepen your guitar knowledge and you buy a guitar music theory book or look up something on the internet you keep bumping into the CAGED system.
Whenever you try to deepen your guitar knowledge and you buy a guitar music theory book or look up something on the internet you keep bumping into the CAGED system. A lot of guitar players use only one pentatonic position / shape: The first position (E shape) it’s because it’s the most comfortable shape to play in.
A lot of guitar players use only one pentatonic position / shape: The first position (E shape) it’s because it’s the most comfortable shape to play in. The harmonic minor scale is often used in neo-classical, gypsy and jazz music.
The harmonic minor scale is often used in neo-classical, gypsy and jazz music.